How Does a Portable Generator Work?
24th Sep 2024
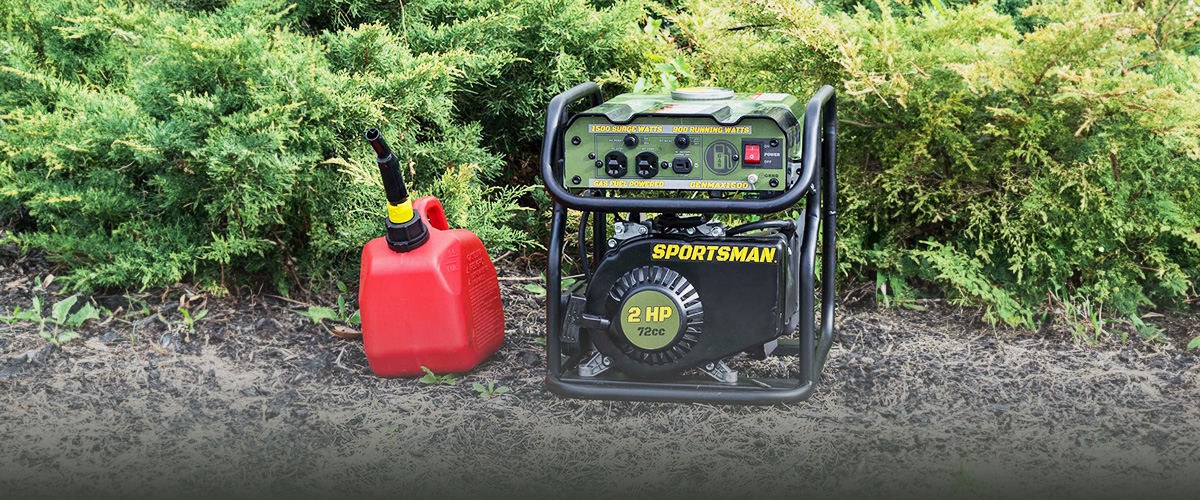

A portable generator is a versatile power solution, serving as a lifesaver during power outages or while enjoying outdoor adventures. These compact devices efficiently convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, offering a dependable backup when your main power supply fails.
Whether you're searching for a portable generator for home use or the best portable generator for camping, understanding how these machines operate is crucial. In this blog, we'll explore the inner workings of portable generators and discuss their various applications in everyday life.
Basic Components of Portable Generator
Portable generators are made up of several critical systems that work in tandem to produce and regulate electrical power. Below, we explore the four main components: each vital to the generator's functionality.
Engine: The engine is the heart of a portable generator, supplying the essential mechanical energy needed to power the system. It operates on various fuel types including gasoline, diesel, or propane.
Alternator: The alternator, composed of a rotor and stator, transforms the mechanical energy generated by the engine into electrical energy. This component is crucial for generating the alternating current (AC) output of the generator.
Fuel system: The fuel system stores and delivers fuel to the engine, enabling smooth operation of the generator. It typically includes a fuel tank, pump, and filter to ensure a steady supply of fuel.
Control panel: The control panel serves as the user interface for the generator, featuring switches, meters, and breakers that allow for precise operation management. It allows users to start the generator and monitor its performance and power output.
How Portable Generator Works?
A portable generator harnesses multiple forms of energy, systematically transforming them through a sophisticated mechanical and electrical process.
Here is an overview of how a portable generator converts stored chemical energy into mechanical and then electrical energy, facilitating essential power output.
1. Combustion Initiation
When the generator's engine starts, it ignites the fuel, which can be gasoline, propane, or diesel. This combustion generates the initial burst of energy required to power the generator. It is the first step in converting stored chemical energy into mechanical energy, setting the stage for subsequent power generation processes.
2. Mechanical Energy Generation
As the fuel burns, it drives the engine's pistons, generating mechanical energy through rotational motion. This energy is crucial as it drives the alternator, which is responsible for electricity generation. The conversion from explosive chemical energy to rotational mechanical energy is foundational in powering the generator.
3. Alternator Activation
The mechanical energy generated by the engine is harnessed to rotate the alternator's rotor, initiating the electricity generation process. This critical step transforms physical motion into energy primed for electrical generation. The efficiency and effectiveness of this step are critical to the overall output of the generator.
4. Magnetic Dynamo Creation
As the rotor spins, it moves within the stator's fixed magnetic field, setting the stage for electrical current generation. This interaction is pivotal as it sets up the conditions necessary for inducing electrical current. The design and alignment of the rotor and stator are engineered to maximize the magnetic interaction.
5. Electrical Current Induction
The movement of the rotor within the stator’s magnetic field induces an electrical current in the stator’s coils. This process is a classic application of electromagnetism, where a changing magnetic field around a conductor induces a current. This step is where the mechanical energy is finally converted into electrical energy.
6. Final Power Output:
The electrical current generated is then directed to the generator’s control panel. This panel is crucial as it regulates the distribution of electricity through various outlets, ensuring the generated power is usable for powering appliances and tools. It marks the endpoint of the energy transformation process, delivering the electricity needed for practical use.
Efficiency of Portable and Inverter Generators
A portable generator converts chemical energy from fuel into mechanical energy through its engine, and then into electrical energy via the alternator, following the law of conservation of energy. This process has an efficiency of about 20-30%, with most energy lost as heat and sound.
Inverter generators enhance this efficiency by adjusting engine speed to match power demands, which conserves fuel, reduces noise, and prolongs the engine's lifespan. This makes them especially suitable for home use and for those seeking a more fuel-efficient and quiet portable generator.
Find Your Perfect Portable Generator at JB Tools!
Whether you're powering up for an outdoor adventure or preparing for an emergency, JB Tools has you covered with our top-notch selection of portable generators and must-have accessories.
From trusted brands like Sportsman to essential items like regulator hoses, parallel cables, and durable covers, we've got everything you need to keep the power flowing. Plus, with fast shipping and free delivery on orders over $99, we've made it easier than ever to get the right equipment at the right price.
Count on JB Tools for all your generator and accessory needs!